What is Mezzanine Debt?
Mezzanine debt (also known as Mezz debt) fills the gap in the capital structure between 1st lien loan and common equity. Since mezzanine funding is considered debt, it takes priority over equity but is still subordinate to the 1st lien mortgage. However, the mezzanine debt is not secured by the property itself. Instead, the mezz debt is secured by an assignment in the borrower’s interest in the entity that owns the property. What does that actually mean? It means that if borrower defaults on the mezz loan, the lender will take control of the entity that purchased the property. This happens much faster than a typical foreclosure, so the borrower must fully know what they’re getting into when using mezzanine financing. Mezzanine loans are typically short in duration, about two to three years with extension rights.
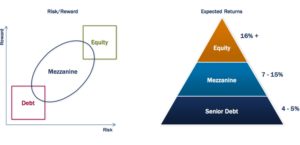
Exhibit 1: Mezzanine Debt in the Cap Stack
Why use mezzanine financing?
One of the biggest benefits of mezzanine debt is it limits equity dilution and allows the sponsor to maintain control of the asset, while capturing all of the upside. Since debt is cheaper than equity, see above exhibit, it keeps the overall cost of capital of the project down. Additionally, the payments to the mezz debt investors are usually fixed, unlike equity which required the investor to participate in the upside of the investment. Please see the example below in Exhibit 2. It is worth noting that the mezzanine debt will require higher interest payments and will leave the owner with less available cash flow.
Exhibit 2: Dilution- Mezzanine Debt vs Outside Equity
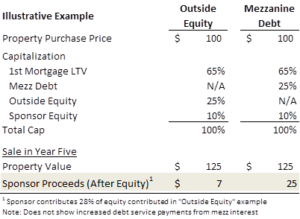
Another benefit of mezzanine debt is that the loan is not defined by standard terms and can be customized to fit the project’s needs. This means that terms are highly negotiated and will require more time to finalize than an 1st lien loan, but also allows the owner to tailor the terms to their specific project, like deferring or eliminating amortization. All terms are up for negotiation. The top factors influencing position in the capital structure and pricing are:
- Quality of the project
- Local market conditions
- Stability of cash flow
- Borrowers capabilities
- Size of loan and duration
Mezzanine debt can be used for a number of different scenarios when gap financing is required. For instance, mezzanine debt can be used to purchase a property outright, ground up development or redevelopment/repositioning. Mezzanine financing can even be used to refinance and restructure an existing capitalization structure, or take out equity partners. Basically, mezz debt is used in any situation where the sponsor would like to close the gap between the first lien mortgage and their equity.
John Femenia
